Self-Supervised Music Motion Synchronization Learning for Music-Driven Conducting Motion Generation
Abstract
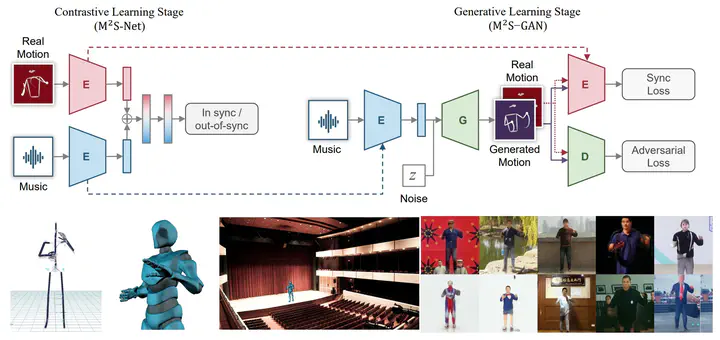
The correlation between music and human motion has attracted widespread research attention. Although recent studies have successfully generated motion for singers, dancers, and musicians, few have explored motion generation for orchestral conductors. The generation of music-driven conducting motion should consider not only the basic music beats, but also mid-level music structures, high-level music semantic expressions, and hints for different parts of orchestras (strings, woodwind, etc.). However, most existing conducting motion generation methods rely heavily on human-designed rules, which significantly limits the quality of generated motion. Therefore, we propose a novel Music Motion Synchronized Generative Adversarial Network (M2S-GAN), which generates motions according to the automatically learned music representations. More specifically, M2S-GAN is a cross-modal generative network comprising four components: 1) a music encoder that encodes the music signal; 2) a generator that generates conducting motion from the music codes; 3) a motion encoder that encodes the motion; 4) a discriminator that differentiates the real and generated motions. These four components respectively imitate four key aspects of human conductors: understanding music, interpreting music, precision and elegance. The music and motion encoders are first jointly trained by a self-supervised contrastive loss, and can thus help to facilitate the music motion synchronization during the following adversarial learning process. To verify the effectiveness of our method we construct a large-scale dataset, named ConductorMotion100, which consists of an unprecedented 100 hours of conducting motion data. Extensive experiments on ConductorMotion100 demonstrate the effectiveness of M2S-GAN. Our proposed approach outperforms various comparison methods both quantitatively and qualitatively. Through visualization, we show that our approach can generate plausible, diverse, and music-synchronized conducting motion. To facilitate future research, both the dataset and experimental codes are open-sourced.